Staff Writer
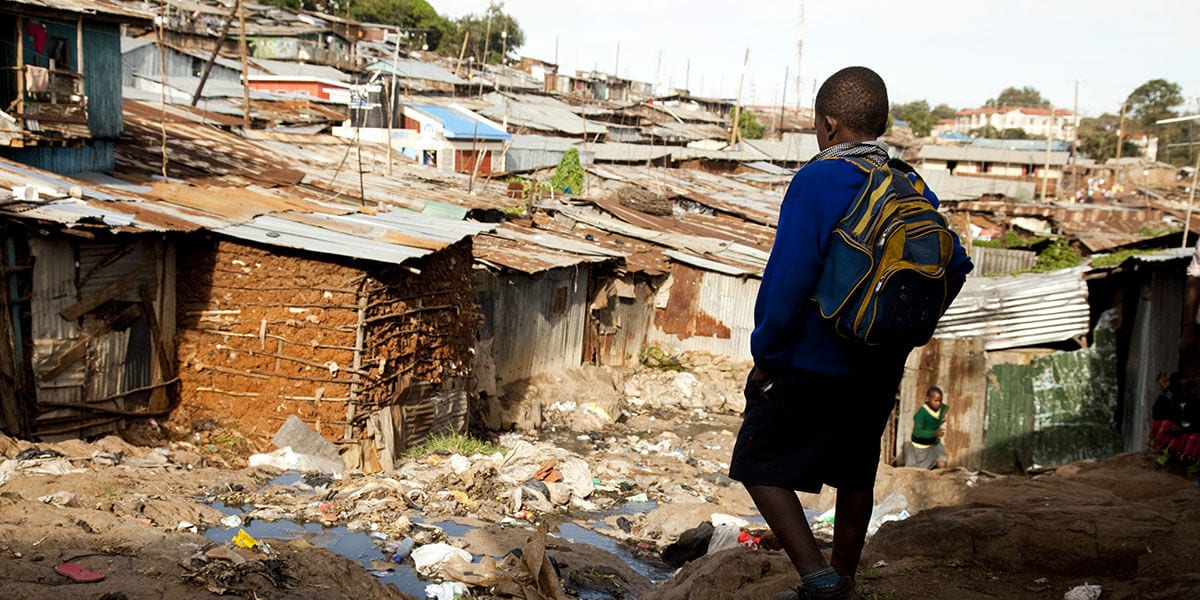
Extreme poverty, defined as living on less than $1.90 per day, is a persistent and widespread problem in Africa. Despite progress in reducing poverty rates in some countries, the number of people living in extreme poverty on the continent remains alarmingly high. In fact, according to the World Bank, over 40% of the population in sub-Saharan Africa lives in extreme poverty, making it the region with the highest poverty rate in the world.
There are a number of factors contributing to the persistence of extreme poverty in Africa. One major factor is the lack of economic opportunity and job creation. Many African countries have high levels of unemployment, particularly among young people, and a lack of access to education and skills training can make it difficult for individuals to find work.
Another major factor is the lack of infrastructure and basic services, such as clean water, healthcare, and electricity. These necessities are often difficult to come by in rural areas and low-income communities, making it harder for people to improve their economic circumstances.
Political instability and conflict can also contribute to poverty in Africa. Countries with ongoing civil wars or political turmoil often struggle with economic development and poverty reduction efforts. This is because conflict can disrupt economic activity and lead to the destruction of infrastructure, which can make it difficult for people to earn a living or access basic services.
In addition, Africa is vulnerable to natural disasters, such as droughts and floods, which can have a devastating impact on communities and economies. These disasters can lead to food shortages and displacement, making it harder for people to escape poverty.
Despite these challenges, there have been some successes in reducing extreme poverty in Africa. For example, the World Bank’s International Development Association has provided funding for poverty reduction programs in a number of African countries. These programs have helped to improve access to education and healthcare, as well as providing microfinance and other economic opportunities for people living in poverty.
There have also been efforts to promote economic growth and development in Africa through foreign investment and trade. For example, the African Union has established the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA), which aims to boost trade and economic integration across the continent.
However, more needs to be done to address the root causes of poverty in Africa and to ensure that economic growth is inclusive and benefits all members of society. This includes investing in education and skills training, promoting entrepreneurship and job creation, and building infrastructure and basic services.
It is also important to address issues of inequality and injustice, as these can perpetuate poverty and make it harder for people to escape it. This may involve efforts to promote gender equality, combat corruption, and address discrimination based on ethnicity or other factors.
Ultimately, reducing extreme poverty in Africa will require a multi-faceted approach that addresses the complex and interconnected challenges facing the continent. It will also require sustained and long-term commitment from governments, development partners, and other stakeholders to ensure that progress is made and sustained over time